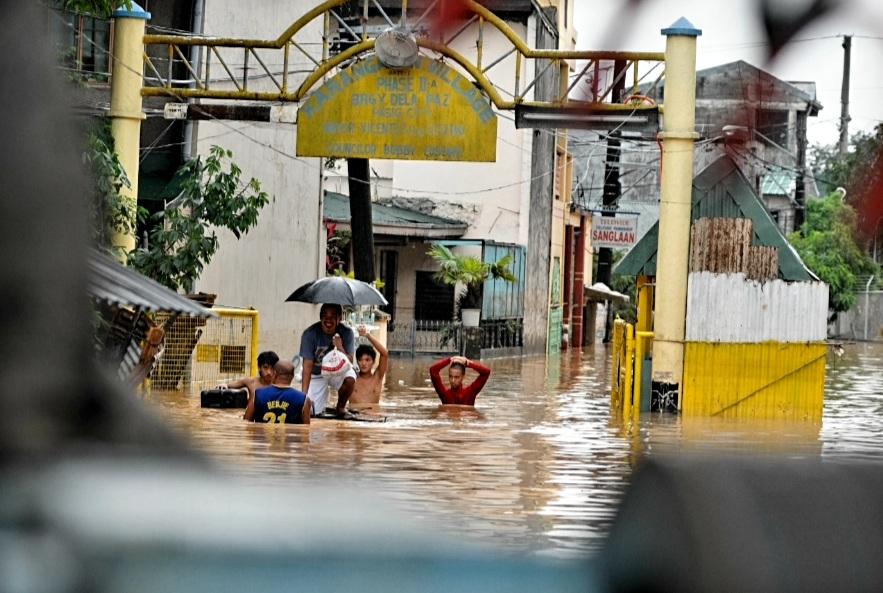
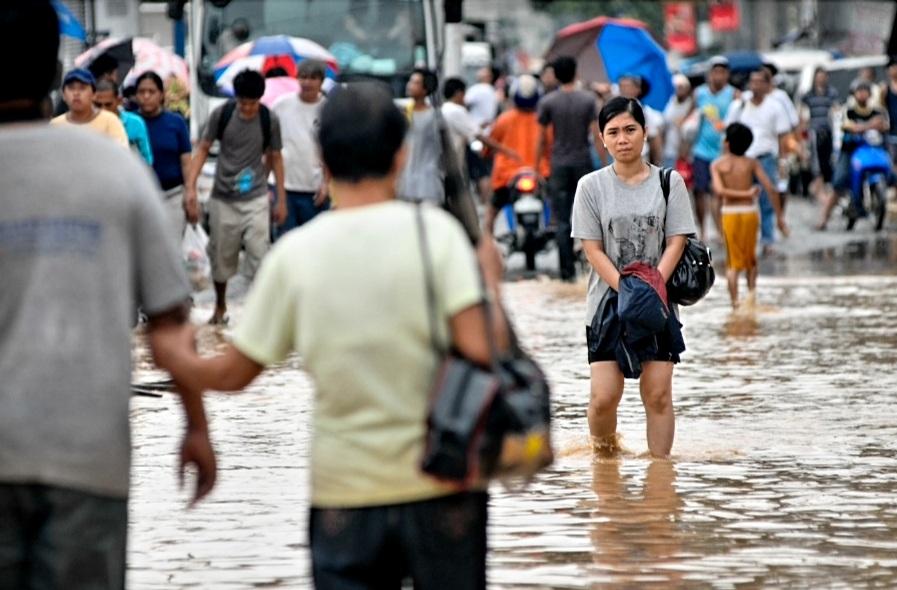
File photo: Flooding brought about by Typhoon Ondoy 2009
The disaster preparation of a community determines a person’s safety during a disaster. No matter how well prepared they are for all possible disasters, all of their efforts will be for naught if their community is unable to respond effectively.
This is why a CDRRMP (community-based disaster risk reduction and management plan) is so important. It assigns the responsibility of disaster preparedness to the entire community, ensuring that organizations, homes, and individuals may work together to make their community more resilient in the case of disaster.
CBDRRMP is critical, especially for countries like the Philippines that are very vulnerable to catastrophes. The Philippines is prone to earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and typhoons due to its location within the Pacific Ring of Fire and typhoon belt. In the 2020 World Risk Index, the country was placed 9th in the world in terms of disaster vulnerability.

One of the most common events experienced by the Philippines is flooding, which underscores the importance of effective floodwater management. There are many ways that local government units are doing this. Efforts range from structural measures such as sizeable underground drainage systems, floodways, pumping stations, flood warning systems, and urban greening to non-structural measures such as minimizing plastic waste, a primary culprit in urban flooding.
With the country situated on five active fault lines, Filipinos must also prepare for earthquakes. It is why many buildings are equipped with earthquake-resistance features. Taking earthquake resilience in the country further are the periodic earthquake drills implemented at the national and organizational levels.
These are good examples of effective CBDRR, where both the authorities and the citizens work together to ensure the safety of life and property in their communities.

SM City Masinag has a rainwater collection tank that can store 17,681 cubic meters of water.
As a trusted and responsible developer of integrated properties, SM has always been committed to promoting Disaster Risk Reduction and Management (DRRM) in its communities, which is evident in many of its malls that employ infrastructure design centered on disaster resilience. SM allocates 10% of its capital expenditures to incorporate disaster-resilient features, of which installing water management design features is one of them.
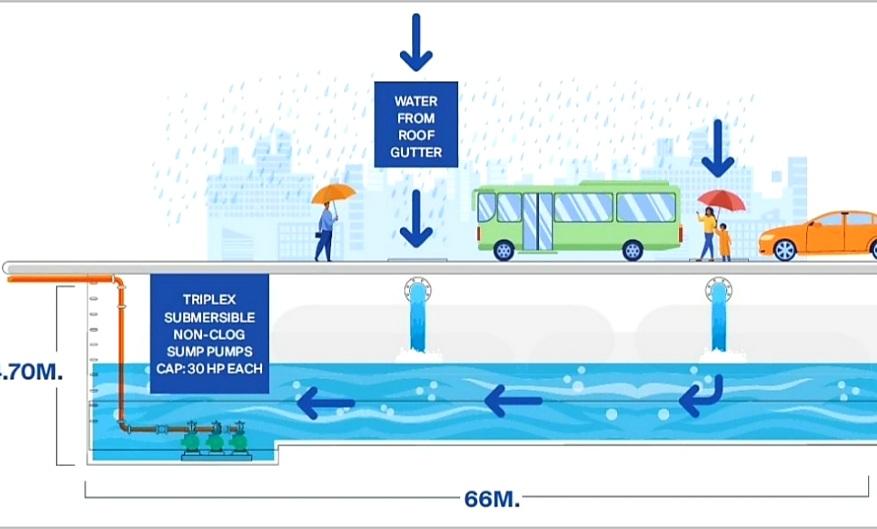
Artist’s illustration of SM’s rainwater collection facility in 22 SM Malls nationwide.
A few examples of these are SM City Marikina, elevated by several rows of concrete stilts to protect tenants and mall-goers during extreme floods. SM Mall of Asia was built with a storm surge barrier for added protection during storm surges, and several malls employ catchment tanks for recycling rainwater.
Across the country, there are 22 SM Malls that have rainwater collection tanks under the mall. All these malls combined can catch and store 79,880 cubic meters of rainwater, equivalent to 32 Olympic-sized swimming pools.
“Wherever SM is, we try to help our communities become resilient to changing weather patterns,” explains Arch. Fides Garcia-Hsu, Vice President of SM Engineering, Design and Development. “Nationwide, we have 22 malls equipped with rainwater catchment facilities that help rain water management to avoid flash floods for surrounding communities.”

SM City Olongapo Central’s rainwater collection tank can hold up to 14,580 cubic meters of water.
Supporting these are several initiatives focused capacity-building for its stakeholders. It includes workshops & learning sessions on Disaster Risk Resilience Management and regular participation in the quarterly national simultaneous earthquake drills for its employees, and the annual Emergency Preparedness Forum for persons with disabilities and the elderly, two of the most vulnerable sectors of society during disasters.
SM Prime has also created long-term ties with organizations that push for a disaster-resilient Philippines, in keeping with its multi-stakeholder strategy. Collaborations include, among others, ARISE-Philippines, the National Resilience Council, the National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Council, the Office of Civil Defense, and the Bureau of Fire Protection.
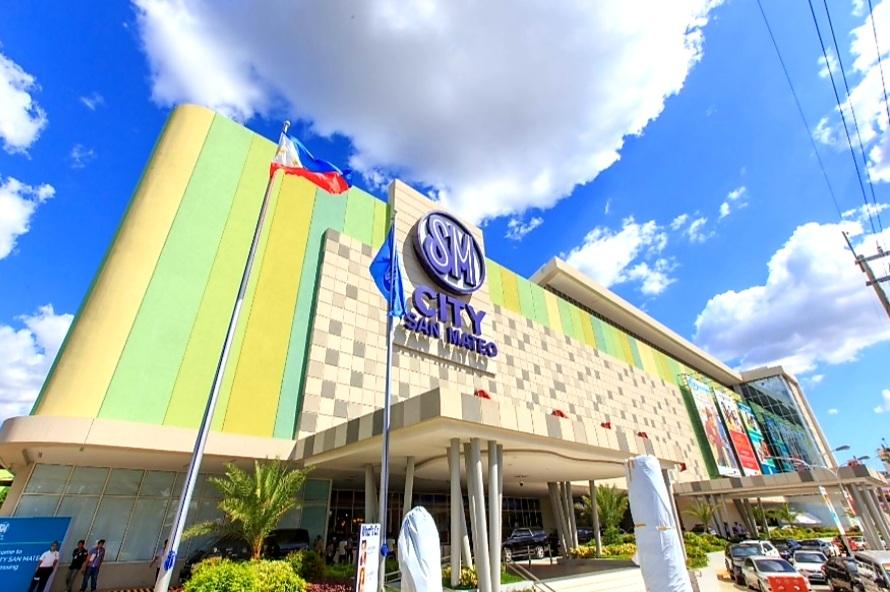

SM City San Mateo’s rainwater collection tank can collect 10,800 cubic meters of potential floodwater.
Visit their website at www.smprime.com for more information on SM Prime Holdings and its other programs towards disaster preparedness
ABOUT SM PRIME HOLDINGS
SM Prime, one of the leading integrated property developers in Southeast Asia, remains committed to its role as a catalyst for economic growth, delivering innovative and sustainable lifestyle cities, thereby enriching the quality of life of millions of people. Sustainability and Disaster Risk Reduction and Resilience form part of SM Prime’s core business strategies. It ensures that its risk-informed investments catalyze sustainable development and positive change in the communities where it operates.